About
Success
Treatment
Financial
Resources
Blog
Contact
Site Tools

Ectopic Pregnancy or Tubal Pregnancy: Everything You Need To Know

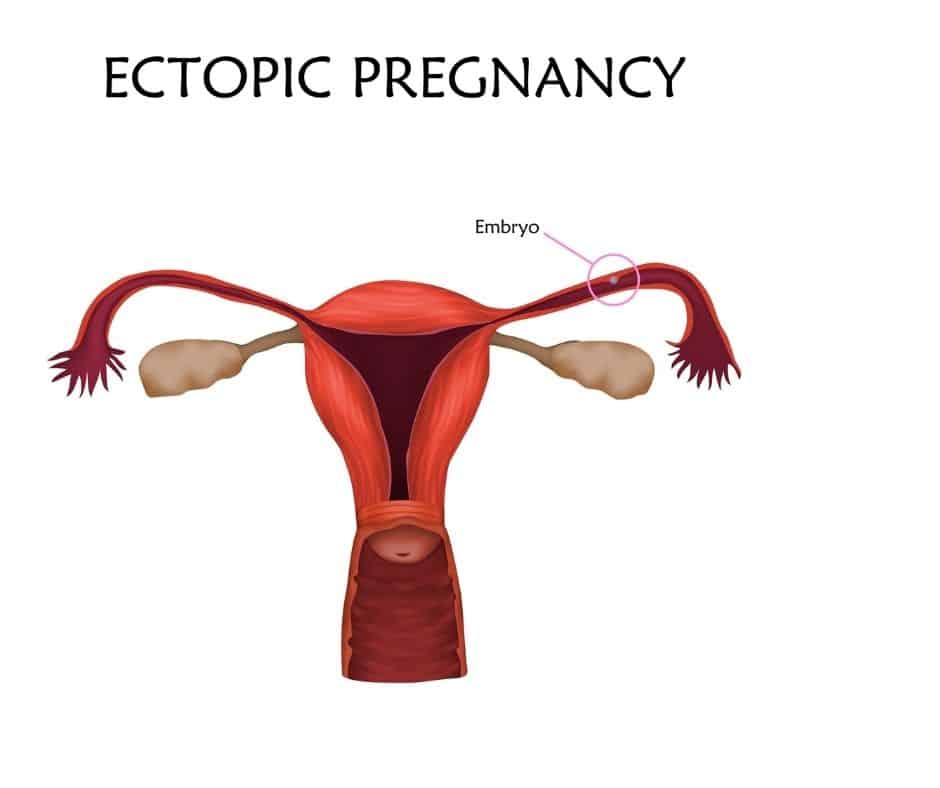
What exactly is an ectopic pregnancy?
An ectopic pregnancy is a pregnancy that grows in other locations outside the womb. It is usually found in the fallopian tubes (the muscular J-shaped tubes in the female reproductive tract).
In a normal pregnancy, the embryo (fertilized egg) implants and grows in the womb. However, in nearly 90% of ectopic pregnancies, the fertilized egg settles in the uterine tubes instead of proceeding on its journey to the uterus. This is the reason ectopic pregnancies are also called “tubal pregnancies.”
Other locations where the embryo can also implant are the cervix, abdomen, and ovary. Hence, it may also be referred to as an abdominal or cervical pregnancy. Depending on the location, it is also called:
- EP
- Tubal pregnancy
- Fallopian tube pregnancy
- Eccyesis
- Extrauterine pregnancy
- EUP
- Abdominal pregnancy
- Cervical pregnancy
Since these locations are not spacious enough and lack the tissue necessary to grow a pregnancy, the fetus will eventually rupture the organs housing it. This may result in heavy internal bleeding, putting the mother’s life in danger. Typically, a tubal pregnancy does not develop into a live birth.
However, ectopic pregnancy is not new. The earliest mention of an ectopic pregnancy in medical records was in 11th century by Al-Zahrawi – a famous Arab physician. The word “ectopic” means “out of place”.
What are the signs and symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy?
The three common symptoms of ectopic pregnancy include amenorrhea (lack of menstruation), abdominal pain, and vaginal bleeding. However, not all women experience all these symptoms. Other possible signs are:
- Pain in the neck, pelvis, shoulder, or abdomen.
- Dizziness or fainting
- Rectal pressure
- Pain on one side of the abdomen
- Vaginal spotting or bleeding
Contact your physician or seek urgent treatment if you are pregnant and are experiencing any of the symptoms above.
What causes an ectopic pregnancy?
Ectopic pregnancy (or tubal pregnancy) occurs when an embryo lodges in the Fallopian tubes or other places outside the uterus, where it is supposed to implant. Any damage, distortion, or scarring of the Fallopian tube can cause a fertilized egg to be stuck inside it.
While the actual cause may be unclear, the following conditions have been associated with ectopic pregnancy:
- Birth defects
- Genetic disorders
- Hormonal factors
- Inflammation and scarring of the uterine tubes due to
- surgery
- an infection or
- medical conditions that change the shape of these tubes and other reproductive organs
What are the likely risk factors?
All women who have sexual intercourse are at risk of an ectopic pregnancy, but the risk increases with any of the following:
- Smoking
- Maternal age of 35 years or older
- History of pelvic inflammatory disease
- History of endometriosis
- Conception happened despite intrauterine devices or tubal ligation
- Conception achieved using fertility medications or procedures
- History of pelvic surgery, abdominal surgery, or multiple abortions
- Anatomical issues in the uterine tubes, which make it hard for the egg to pass through them.
- History of previous ectopic pregnancy
How these risk factors increase the chances
Age
Any woman – no matter the age – who ovulates and has intercourse with a male partner can have an ectopic pregnancy. However, women aged 35 to 44 are at the greatest risk of developing the condition.
History
A previous history of ectopic pregnancy is the biggest factor that can increase your risk of having another case.
Fallopian tube issues
Disruption of the normal anatomy of the Fallopian tubes can cause ectopic pregnancy in the tubes or other areas.
Previous surgeries
If you have had surgery on the fallopian tubes, it can cause scarring and disruption of the normal structure of these tubes, increasing the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Infections
Pelvic infection is another factor that can increase your chances of having an ectopic pregnancy. Although these infections are usually caused by sexually transmitted bacteria, such as chlamydia or N. gonorrhea, bacteria transmitted through other means can also cause them. Infection may result in an ectopic pregnancy by obstructing or destroying the fallopian tubes.
The inner lining of the uterine tubes contains tiny hair-like projections referred to as cilia, which help the egg move through the tubes into the uterus. Any damage to these cilia due to infection can disrupt the transportation of eggs in the fallopian tubes. Hence, a fertilized egg may become trapped in the tubes, resulting in an ectopic pregnancy.
Infection can also lead to scarring and blockage of the fallopian tubes, stopping the eggs from reaching the womb.
Having two or more sex partners
Since having multiple sex partners raises a woman’s risk of developing pelvic infections, your odds of ectopic pregnancy may increase when you have more than one sex partner.
Gynecological conditions
Conditions like fibroid tumors, pelvic scar tissue (pelvic adhesion), or endometriosis can make the uterine tubes narrow and impede egg transport, increasing the likelihood of a tubal pregnancy.
Use of IUD (intrauterine device)
About 50% of pregnancies in women who use IUDs will occur outside the uterus. However, the number of women getting pregnant when using intrauterine devices is pretty low. So, the probability that IUD use will cause an ectopic pregnancy is low.
Cigarette smoking
Smoking cigarettes around the fertile period can also increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy. Researchers found that this risk depends on the dose. This means that a woman’s risk of ectopic pregnancy is dependent on her habits and increases the more cigarettes she smokes.
Infertility
A history of long-term infertility can also be associated with a higher risk.
Other likely causes
Fallopian tube tumors, infection, or birth defects can raise a woman’s chances of an ectopic pregnancy.
What percentage of women have an ectopic pregnancy?
About 1-2% of all pregnancies occur outside the womb.
What tests, exams, or procedures can diagnose ectopic pregnancy?
If you are suspecting that you may have an ectopic pregnancy, consult your physician as soon as possible. While ectopic pregnancy cannot be detected through a physical examination, your doctor may still conduct one to rule out other possible factors.
Preliminary doctor consultation
Diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy usually begins with an interview and physical examination by a doctor. This is then followed by a quantitative (measures hormone levels) or qualitative (positive or negative for pregnancy) pregnancy test.
Pregnancy tests and ultrasound
In some cases, the doctor may notice a tender mass in the pelvic exam. If it is suspected to be an ectopic pregnancy, blood hormone pregnancy tests and a pelvic ultrasound are done to confirm the diagnosis. Transvaginal ultrasound is a very useful test to check for an ectopic pregnancy. During this test, the doctor inserts a small probe into the vagina, and pelvic images can be seen on the monitor.
Although transvaginal ultrasound can show the gestational sac in a normal or an ectopic pregnancy, the findings are not always conclusive. The ultrasound can also reveal if there’s no pregnancy inside the womb.
Laparoscopy
In some rare cases, laparoscopy may be required to establish a diagnosis of an ectopic pregnancy. In a laparoscopic procedure, imaging instruments are inserted into the body via tiny incisions in the abdominal wall to see the reproductive structures in the pelvis and abdomen, hence showing the location of the ectopic pregnancy.
Pregnancy hormone tests
Your physician might also conduct a blood test to check your levels of pregnancy hormones such as progesterone and human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG). If the levels of these hormones begin to reduce or remain the same for many days and a gestational sac is not seen during an ultrasound, the pregnancy may be ectopic.
If you’re experiencing severe symptoms like vagina bleeding or pain, you may not have enough time to undergo all these diagnostic tests. The Fallopian tubes may rupture, resulting in internal bleeding. In cases like this, your doctor will carry out an emergency surgery to provide urgent treatment.
Treating ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancies can endanger the mother’s life. Plus, the embryo can’t develop into a live birth. Hence, it’s important to quickly remove the embryo for the mother’s health and future fertility. There are many treatment options to consider based on the site of the ectopic pregnancy and its development.
Medication
If your doctor thinks that immediate complications are very unlikely, he or she may suggest you take medications to prevent the ectopic mass from rupturing. One common drug for this is methotrexate (also known as Rheumatrex).
Methotrexate is a medication that inhibits the growth of actively dividing cells, including the cells of the ectopic mass. It is usually administered in the form of an injection. You may also need to undergo some blood tests to know if the drug is working. If it is, you are going to notice menstruation-like symptoms, including:
- Cramping
- Passing of tissue
- Bleeding
Further surgery is not usually required once this occurs. Unlike surgery, the use of medication like methotrexate does not carry the risks of fallopian tube damage. However, you may be unable to get pregnant for months after using this drug.
Surgery
A laparotomy may be repeated if the surgery failed the first time, but this time a large abdominal incision will be used. Your physician may also have to remove the fallopian tube completely if it is severely damaged.
Home care
Your doctor will provide you with instructions concerning the care of your abdominal incisions following surgery. It is important to ensure the incisions are kept dry and clean while they heal. So, make sure to check them every day for signs of infection, such as:
- Continuous bleeding
- Swelling
- Redness
- Hot to touch
- Bad-smelling drainage from the incision site
You can also have some light vagina bleeding and blood clots post-surgery. This may continue up to six weeks after your surgery.
Below are other self-care measures you can take:
- Don’t lift anything weighing more than 10 pounds
- Drink a lot of fluids to prevent constipation
- Get pelvic rest. This may mean abstaining from sex, douching, and use of tampons.
- Have plenty of rest in the first week after surgery and only increase physical activity in the following weeks as allowed
- Make sure to inform your physician if you feel more pain or think something is out of normal
Prevention
Sadly, it is not always possible to predict and prevent an ectopic pregnancy. However, you can lower your risk of developing the condition by maintaining good fertility health.
To minimize your chances of contracting sexually transmitted diseases (STD), always insist that your partner use a condom during intercourse and reduce your number of sexual partners. This is because STDs can cause pelvic inflammatory disease – a condition that causes the fallopian tubes to be inflamed.
Visit your doctor on a regular basis and undergo gynecological examinations and STDs screenings as necessary. Another way to prevent ectopic pregnancy is to take steps to enhance your personal health by quitting alcohol, smoking, drug use, etc.
Surgical removal of ectopic mass can cause scarring of the fallopian tubes, raising the odds of having another ectopic pregnancy. If you have to remove one or both fallopian tubes, speak with your physician about possible fertility treatments, such as in-vitro fertilization (IVF), before undergoing any surgery.
Dealing with fertility issues after ectopic pregnancy
Whether it occurs in the first few weeks or later, pregnancy loss can be very devastating. You can ask your physicians if there are any support groups that can provide necessary emotional support and guidance during this difficult time. Take
good care of yourself by having enough rest, consuming healthy foods, and exercising moderately. Also, remember to give yourself enough time to grieve and process the loss.
Take away
The good news a lot of women with a history of ectopic pregnancy go on to have healthy pregnancies in the future. As long as one of the fallopian tubes is still intact, eggs can be fertilized as usual. But if you already have a reproductive problem, it can impact your future fertility and raise your chances of developing an ectopic pregnancy. This is especially true if the preexisting problem was the cause of the previous ectopic pregnancy.
When you’re ready to try again for a baby, ask your physician about ways to make sure your future pregnancy is a healthy one.
Coastal Fertility Medical Center has helped many hopeful couples overcome ectopic pregnancy risks and become parents. Schedule a consultation today to learn more from our fertility specialists.
Related Post
-
What is Azoospermia – Types, Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
-
15 Things Doctors Want Women in Their 30s to Know About Their Fertility
-
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS) – Causes, Risks, and Treatments
-
This IVF Pregnancy Success Video Is Going Viral On TikTok, And It’s The Most Adorable Announcement
-
End your week with these happy and heartwarming stories and videos
-
Fertility clinic shares IVF pregnancy success with parents-to-be in adorable video
Halloween 2019
Each year, Coastal Fertility Medical Center’s staff hosts a fun get together for our former patients and their families. View more photos from our 28th annual Miracle Babies Halloween event!Popular Searches
- Orange County Fertility Clinic
- Irvine, California Fertility Center
- Coastal Fertility Medical Center
- Free Fertility Seminar, Irvine CA
- In Vitro Fertilization and ICSI
- Best Orange County Infertility Doctor
- Southern California Fertility Specialist
- PGD, PGS Orange County
- Egg Donation and Surrogacy
Address
Coastal Fertility Medical Center15500 Sand Canyon Avenue
Suite 100
Irvine, CA 92618
©2024 | Sitemap | HIPAA/Privacy | Disclaimer and Privacy Policy
News from our Top Doctors

Our fertility clinic focuses on helping you build your family regardless of your sexual orientation or the gender you choose to identify with. We are even taking further steps to make LGTB people feel more welcome at our fertility clinic. Each of our patient-facing staff goes through LGTB training to let family-building clinicians provide necessary support and make you feel highly welcome.

Coastal Fertility Medical Center offers one of the most advanced fertility treatments and is completely transparent regarding the costs of procedures and any other expenses that you may have to pay before commencing your treatment. This differentiates us from some fertility clinics that reduce prices before the signing of the contract but charge you extra later on. We make sure our patients are well aware of any possible extra pricing that may occur over the course of their treatment.

The infertility industry is currently segmented, with each service or treatment being handled by a different provider. Our all-inclusive model simplifies an otherwise complex and difficult process. We are here to revolutionize the infertility industry by offering a one-stop-service model to assist our patients through infertility challenges while reducing physical, emotional, and financial risks.

Our globally respected team of specialists are helping improve IVF technologies to enter into a generation of better outcomes for infertility. Although you’ll have a doctor guiding you, you are also going to benefit from the experience and insights of other doctors during case review collaboration meetings, which take place every week. So, you won’t just rely on the expertise of a specialist but benefit from the knowledge of many reputed fertility experts.

Our team specializes in difficult cases and help patients who may have been considered “hopeless” at other fertility clinics. Thanks to our personalized solutions, expertise, and internal collaboration, weare able to maximize pregnancy success rates that are well above the industry average, even in difficult infertility cases.

We know that every situation is different and that everyone requires different treatments. Unlike facilities that take “a one-size-fits-all” approach for all cases, our fertility specialists use more than 40 customized protocols to raise the chances of success. The customized approach even extends to our fertility laboratory. Our on-site lab director and his highly-experienced team nurture every embryo and egg to increase the odds of success of each cycle.

Coastal Fertility Medical Center offers one of the most advanced fertility treatments and is completely transparent regarding the costs of procedures and any other expenses that you may have to pay before commencing your treatment. This differentiates us from some fertility clinics that reduce prices before the signing of the contract but charge you extra later on. We make sure our patients are well aware of any possible extra pricing that may occur over the course of their treatment.
Thanks for Joining!
We will be sending new updates soon.
You’re all set!
Your new patient forms have been submitted and received. We look forward to seeing you at your appointment.
Send us a message, we’ll be happy to answer any questions!
Please complete the form so we can best serve and help you with your journey towards parenthood.
On Demand Seminar Registration
Following the Preimplantation Genetic Screening process, which helps ensure there are normal chromosome numbers and detects possible genetic disorders, the most healthy embryo(s) are selected to be implanted into your or your chosen surrogate’s womb. 2 weeks after the transfer of the embryo, your physician will conduct a final blood test to determine the level of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) in your body. Increased hCG levels usually indicate a positive pregnancy test.
For fertilization to take place, the collected egg and sperm are combined in a petri dish and cultured in an embryo incubator. This dish is closely watched to check whether any of the eggs have been fertilized. Once the egg is fertilized, it is referred to as an embryo or a blastocyst on the 5th day of development. Our in-house embryologist carefully nurtures every embryo to the right time, even if it means working outside the standard business operating hours. For instance: If an oocyte is not mature, our laboratory will wait for it to mature and then ICSI it at the right time.
The egg retrieval is a slightly invasive medical procedure that takes about 20 to 30 minutes. You will be given an anesthetic to make you sleep for the duration of the procedure. Using ultrasound technology, your doctor will harvest your eggs transvaginally with a small, hollow needle connected to an ultrasound probe. Once your eggs are collected, your partner’s semen or donor sperm you have pre-selected is used for fertilization. The sperm are washed and prepared, and the top-quality sperm extracted is used to fertilize the eggs.

Your doctor will create a customized medication schedule that contains information about the fertility medications and hormone injections you have to take. Medication and injections are taken to encourage your ovaries to mature a large number of eggs for fertilization. Since women don’t respond to fertility drugs and hormones the same way, personalized protocols are crucial to the IVF cycle success. At Coastal Fertility, we will monitor you closely, letting you understand the changes occurring in your body and keeping track of how your egg follicles are growing.

On-site consultations typicallyinclude a standard fertility evaluation, consisting of a physical examination, complementary follicular ultrasound, and testing to enable your doctor to know your present fertility status and draw up a treatment plan.

This consultation includes a detailed medical evaluation with a doctor. You and your physician will review your health records and have enough time to talk about your goals and get answers to your questions. We recommend that you jot down all your questions before the visit to allow you to make the best use of the time spent with your doctor.

Your Reproductive Endocrinologist will take all factors into consideration and create a comprehensive plan of care, otherwise known as the treatment plan. This plan will include treatment recommendations from the physician and enable your financial coordinator to make a precise quotation once you meet.

Our globally respected team of specialists are helping improve IVF technologies to enter into a generation of better outcomes for infertility. Although you’ll have a doctor guiding you, you are also going to benefit from the experience and insights of other doctors during case review collaboration meetings, which take place every week. So, you won’t just rely on the expertise of a specialist but benefit from the knowledge of many reputed fertility experts.

The infertility industry is currently segmented, with each service or treatment being handled by a different provider. Our all-inclusive model simplifies an otherwise complex and difficult process. We are here to revolutionize the infertility industry by offering a one-stop-service model to assist our patients through infertility challenges while reducing physical, emotional, and financial risks.
Our fertility clinic focuses on helping you build your family regardless of your sexual orientation or the gender you choose to identify with. We are even taking further steps to make LGTB people feel more welcome at our fertility clinic. Each of our patient-facing staff goes through LGTB training to let family-building clinicians provide necessary support and make you feel highly welcome.

We know that every situation is different and that everyone requires different treatments. Unlike facilities that take “a one-size-fits-all” approach for all cases, our fertility specialists use more than 40 customized protocols to raise the chances of success. The customized approach even extends to our fertility laboratory. Our on-site lab director and his highly-experienced team nurture every embryo and egg to increase the odds of success of each cycle.
Our team specializes in difficult cases and help patients who may have been considered “hopeless” at other fertility clinics. Thanks to our personalized solutions, expertise, and internal collaboration, weare able to maximize pregnancy success rates that are well above the industry average, even in difficult infertility cases.

Upon your arrival, you will check in with a Patient Care Coordinator. We will obtain your insurance information for benefits verification, a copy of your identification and take a picture for your electronic medical chart
Welcome to Coastal Fertility Family
Coastal Fertility is the leading provider of fertility solutions located in Orange County. Join us to get free updates on fertility news, treatments, infertility solutions and more.
Welcome to Coastal Fertility Family
Coastal Fertility is the leading provider of fertility solutions located in Orange County. Join us to get free updates on fertility news, treatments, infertility solutions and more.